
The fact that there was no jitter is what gives this service such a high value in CapLoader’s “Periodicity” column. This means that a new connection will be made to the Cobalt Strike C2 server every minute.
The output from Didier’s 7868.py tool looks something like this:Ġx0001 payload type 0 windows-beacon_http-reverse_httpĠx0008 server,get-uri '103.207.42.11,/ca'Īs you can see, it uses HTTP for transport with a “sleeptime” of 1 minute (60000 ms) and 0% jitter. I expected this feature to detect Cobalt Strike traffic in HTTP, but I was delighted to see that CapLoader often detects even TLS encrypted Cobalt Strike beaconing with really good precision!Īs shown in the video, the Cobalt Strike beacon config can easily be extracted from the network traffic using The detection of Cobalt Strike inside of HTTP and SSL traffic was recently introduced in the latest It is more common, however, for CapLoader to yield false negatives, which means that it can't identify the protocol. Some days ago I've published some informations about CobaltStrikeScan 1, a useful tool to identify Cobalt Strike beacons in processes memory, today l'd like to share a couple of resources useful to understand how detection works.
#HOW TO DETECT COBALT STRIKE BEACON UPDATE#
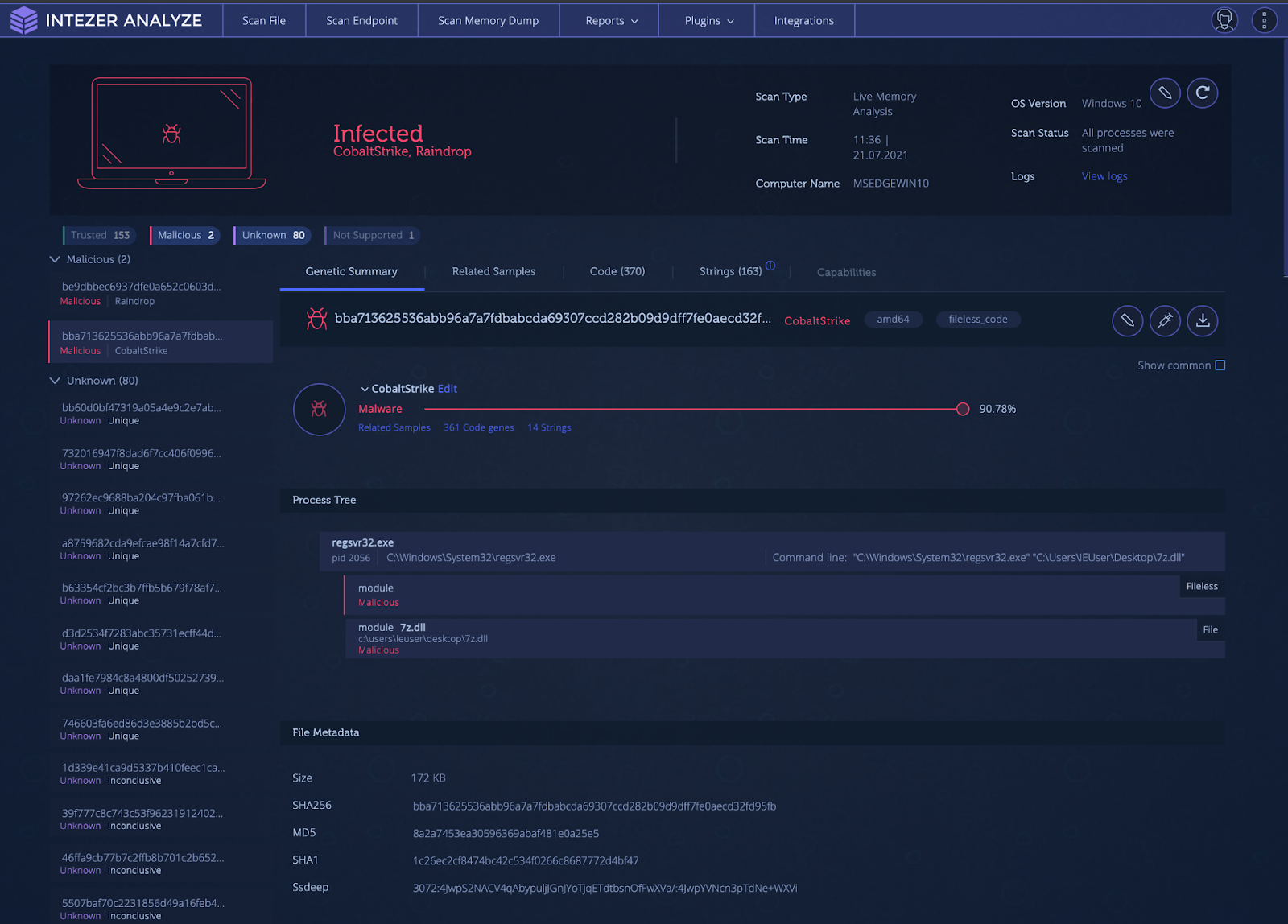
the protocol classification that CapLoader gives a flow or service might be wrong. A brief update on Cobalt Strike detection in forensics analysis, with a couple of new resources. This means that there can be false positives, i.e. The third service in this list is also very periodic, that’s the Hancitor trojan beaconing to its C2 server every two minutes.ĬapLoader uses machine learning to identify the application layer protocol based on the behavior of the traffic, not the port number. The capture file I’m looking at is called “-Hancitor-traffic-with-Ficker-Stealer-and-Cobalt-Strike.pcap” and can be downloaded from here:ĬapLoader’s Services tab shows us that the connections to TCP 80 and 443 on 103.207.42.11 are very periodic, with a detected period of exactly 1 minute.ĬapLoader successfully identifies the protocols for these two services as Cobalt Strike over HTTP and Cobalt Strike over SSL, respectively.
#HOW TO DETECT COBALT STRIKE BEACON WINDOWS#
Windows Sandbox, which just takes a couple of seconds to deploy and run. I have also taken the precaution of analyzing the PCAP file in a 😱 OMG he’s analyzing Windows malware on a Windows PC!!! Your browser does not support the video tag. This video shows how Cobalt Strike and Hancitor C2 traffic can be detected using CapLoader. If Network Beacon Scores goes above threshold, BeaconHunter will automatically suspend the thread.Detecting Cobalt Strike and Hancitor traffic in PCAP (Note: There is probably a better way, but it works)
Install-Package ConsoleTables -Version 2.4.2 Recently I’ve already written about Cobalt Strike detection during forensics analysis.This opens up a world of possibility for post-exploitation. Import a script into Beacon and invoke its cmdlets at will. Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console Cobalt Strike's Beacon now has the ability to work with PowerShell. Or git clone and go to Release folder.NET Framework version Log, display, and take action against them. Then, leverage ETW tracing to specifically monitor suspicious thread activity: Find all processes that contain a thread in a Wait:DelayExecution state. Red teamers can use this tool to research ETW bypasses and discover new processes that behave like beacons.Īuthor: Andrew Oliveau implants injected in a benign process live in a thread with a Wait:DelayExecution state (probably related to Cobalt Strike's sleep). Blue teamers can use this tool to detect and respond to potential Cobalt Strike beacons. Behavior based monitoring and hunting tool built in C# tool leveraging ETW tracing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
